The study includes a comparative analysis of traditional and innovative methodologies, such as learning through provocation and digital mentoring. The presented data demonstrate the advantages of these approaches in reducing adaptation time, increasing task accuracy, and enhancing employee engagement in the learning process. The significance of personalized training and interactive technologies is emphasized.
The research findings confirm the necessity of integrating digital solutions into corporate training systems. Future research prospects include the development of new immersive methodologies, the use of artificial intelligence in learning, and the analysis of the long-term impact of digital educational strategies on employees professional growth.
Introduction
In today’s world, where technology is rapidly changing traditional business processes, the question of effective employee training and development takes on a new significance. Digital transformation is no longer a concept for the future but has become a daily reality that demands flexibility, adaptability, and constant updating of knowledge. Companies aiming for sustainable growth and competitiveness are forced to reconsider established approaches to employee training by implementing innovative strategies that not only transmit knowledge but also foster critical thinking, the ability for self-development, and the capacity to apply acquired skills in new, often unconventional situations.
This issue becomes particularly relevant in light of the accelerating digitalization of work processes. Artificial intelligence, automation, big data analytics, and virtual reality technologies are reshaping traditional models of interaction within organizations. Conventional training methods, based on linear information acquisition and sequential competence development, no longer meet the needs of the dynamic market. At the same time, the mechanical implementation of technological solutions without considering the individual and organizational characteristics of employees can lead to a formal but ineffective development process.
The aim of this research is to identify and analyze innovative approaches to employee training in the context of digital transformation, assess their effectiveness, and identify potential barriers to their implementation. To achieve this, it will be necessary not only to consider modern technologies and methods but also to analyze the influence of organizational culture, psychological aspects of knowledge perception, and adaptation mechanisms. Unlike most studies focused on traditional methodologies, this work will emphasize interdisciplinary methods. These include cognitive modeling, which allows predicting the individual development trajectories of employees, and network analysis methods, which help identify hidden connections and interactions within the learning group.
Moreover, significant attention will be given to empirical research based on immersive technologies. The use of virtual simulations and adaptive algorithms for personalized learning is becoming not just a convenient tool but a necessary condition for forming flexible and sustainable professional skills. The study will also look at neurofeedback mechanisms used to assess employees cognitive load during training, as well as the concept of «learning through contradiction», where the development of competencies occurs through conscious immersion in problem situations.
Thus, the research covers a wide range of issues, from the theoretical foundations of digital learning to the analysis of specific practices and their impact on employee performance. Innovative approaches should not only complement existing methods but also transform the system of professional development itself, making it more adaptive, personalized, and focused on long-term competency development.
Digital transformation and its impact on the training system
Digital transformation is fundamentally changing the landscape of corporate training by introducing advanced technologies and innovative approaches into employee development processes. These changes reflect the desire of organizations to adapt to rapidly changing market conditions and technological innovations.
Modern technologies offer new opportunities for corporate training, making it more flexible, personalized, and effective. The development of mobile devices enables employees to access learning materials anytime and anywhere, significantly enhancing the individualization of the learning process. Immersive technologies, including virtual and augmented reality, create a fully immersive experience, allowing real-world work situations to be simulated and professional skills to be practiced in a safe environment [1].
The application of artificial intelligence and big data analytics enables adaptive learning, which adjusts to the individual needs and preparation level of each employee. Social learning, in turn, is based on the integration of social platforms and collaborative tools, fostering knowledge and experience sharing among colleagues and strengthening collective interaction [2].
Another important trend is microlearning, which involves the use of short, focused learning modules. This approach allows for quick acquisition of specific skills or knowledge, which is especially relevant in the context of limited time and the high dynamics of work processes [3]. Additionally, microlearning can enhance learner engagement by providing content that is easily digestible and accessible on-demand. As a result, organizations can foster a culture of continuous learning that aligns with the fast-paced nature of modern workplaces. To visually illustrate the distribution of these trends, we present a pie chart displaying their share in the overall volume of digital initiatives in corporate training (Figure 1).
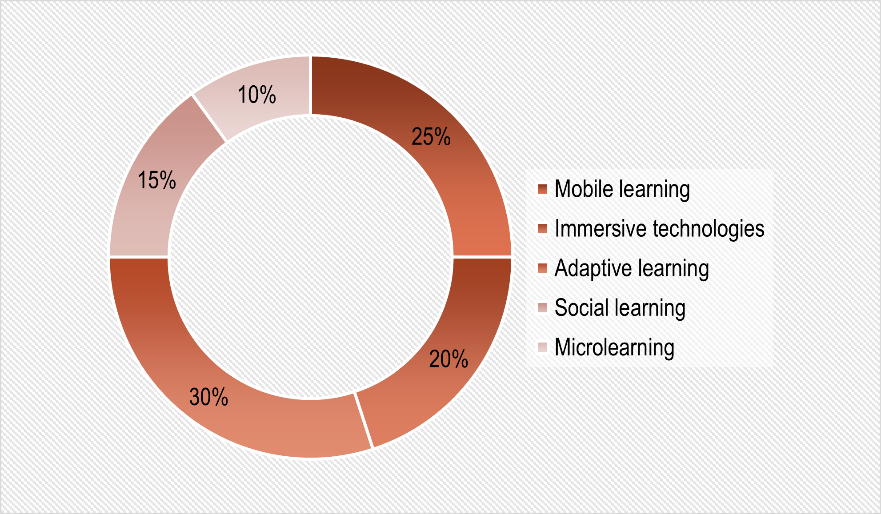
Figure 1. Distribution of digitalization trends in corporate training.
These data demonstrate that the most significant areas are adaptive learning and mobile learning, highlighting the companies drive for personalization and flexibility in educational processes.
However, the implementation of new technologies in learning is accompanied by various psychological and organizational factors that influence their perception and effectiveness. Among the psychological factors, one can note the level of digital literacy of employees, their readiness for change, and their perception of technologies as useful tools or, on the contrary, as threats. Organizational aspects include support from management, the availability of infrastructure, and a culture of continuous learning [4].
For a more detailed analysis, let’s present a table reflecting the key psychological and organizational factors affecting the perception of new technologies in learning (Table 1).
Table 1
Psychological and organizational factors in perceiving new technologies in education
| Factor | Description | Example |
| Readiness for change | Openness of employees to new working methods and learning. | Flexible employees adopt and master innovative training approaches more quickly. |
| Support from management | Active involvement and encouragement of new technology use by management. | Leaders who implement new technologies and motivate their teams to use them facilitate successful adoption. |
| Organizational culture | The extent to which an organization encourages innovation and continuous learning. | Companies with a culture of ongoing development find it easier to implement new educational technologies. |
| Availability of necessary infrastructure | Provision of technical conditions for the implementation and use of new technologies. | Lack of stable internet connection hinders the use of online courses. |
| Social influence | The impact of colleagues and the environment on attitudes towards new technologies. | Positive feedback from colleagues about a new platform increases the willingness of other employees to use it. |
The analysis of the presented factors demonstrates that the successful implementation of digital technologies in corporate training depends on a balanced combination of psychological and organizational aspects. Support from management and a favorable organizational culture contribute to the rapid adoption of innovations, while insufficient technical infrastructure and negative previous experiences can significantly slow down this process. Companies that recognize the importance of these factors can proactively develop adaptation strategies, including programs to improve digital competencies, the implementation of flexible learning platforms, and the creation of a comfortable environment for experimenting with new methods. Ultimately, the more thoughtfully technology is integrated, the more effective its perception will be, and the higher employee engagement in the learning process will be.
The analysis of trends in digital transformation and factors affecting the perception of technologies in learning emphasizes the need for deeper and more effective solutions. Modern realities require companies not just to implement digital tools, but to create fundamentally new learning methods that can not only transfer knowledge but also form critical thinking, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to changing conditions in employees. In this context, innovative approaches such as learning through provocation and mentoring with the use of digital twins represent promising models capable of significantly enhancing professional development effectiveness.
Innovative approaches to employee training
Modern training methodologies are evolving in response to the new challenges of digital transformation. They are no longer purely informational but have taken on an interactive, adaptive, and even emotionally engaging nature. In this context, new technologies and models are emerging that allow not only to transmit knowledge but to immerse employees deeper in the process of mastering it, creating conditions for active participation and critical reflection.
One of these methods is learning through provocation, which has developed at the intersection of cognitive psychology and educational technologies. Historically, this approach emerged in the late 20th century in academia when researchers began studying the influence of paradoxical situations on the speed and depth of information absorption [5]. Subsequently, this method found practical application in the corporate sector, especially in training leaders and specialists who make decisions in uncertain conditions.
The essence of the method is creating situations that provoke cognitive dissonance or unconventional thinking in learners. These may be scenarios in which familiar solutions don’t work, logic seems broken, and there is no single correct answer. In such conditions, the employee is forced to analyze the problem from different perspectives, search for alternative solutions, and experiment with new strategies. Practical examples include tasks in which a group of participants faces an artificially created resource limitation or time pressure that requires immediate solution finding in unconventional circumstances.
The effectiveness of this approach is supported by research on cognitive processes, according to which unexpected and complex tasks activate deeper levels of thinking and contribute to better retention of information [6].
Traditional training methods, including lectures, presentations, and linear curricula, ensure an average level of information retention at 60% two weeks after completing the course [6]. The main problem with this is the reduction in interest in learning and insufficient employee engagement.
In contrast, the learning method through provocation, based on creating situations with a high degree of uncertainty that require active employee involvement in the solution search process, shows significant improvement in results. On average, the level of information retention reaches 85%, which is 25 percentage points higher than with traditional approaches [7].
This is explained by the fact that emotionally engaging and intellectually stimulating tasks promote more active cognitive activity, which improves the retention and awareness of acquired knowledge.
To demonstrate the influence of provocative methods on the speed of knowledge acquisition, we can look at the data from empirical studies, presented in the following graph (Figure 2).
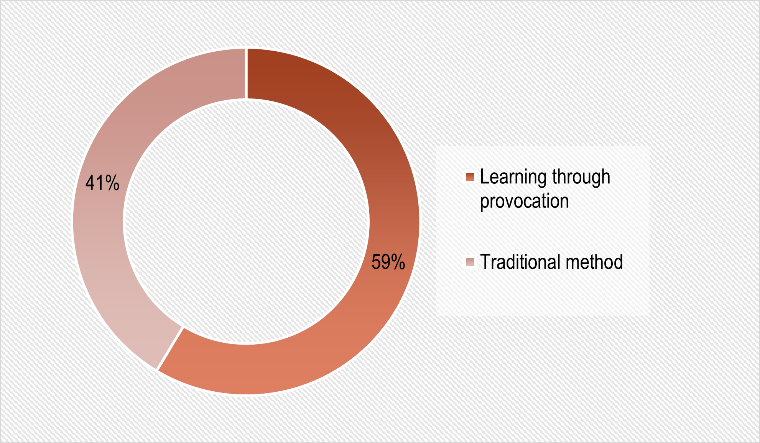
Figure 2. The rate of information retention using provocative learning methods compared to traditional methods.
The analysis of the data demonstrates the high effectiveness of the learning method through provocation compared to traditional forms of training. This approach not only accelerates the information acquisition process but also promotes the development of critical thinking, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to non-standard situations in employees.
Another important direction in the development of corporate training is mentoring with the use of digital twins. This technology originates from the concept of digital avatars, which were initially used in industrial process modeling [8]. However, over time, the idea of virtual replicas of specialists transitioned into the field of education and professional training. Between 2018 and 2020, several technology companies began developing software solutions that allowed the creation of personalized digital copies of experts to transfer knowledge and skills to less experienced employees [9]. The core idea of digital mentoring is the creation of artificial intelligence based on the knowledge and experience of real mentors. These digital twins can analyze the behavior of the learner, provide recommendations, adapt training materials based on progress, and even engage in real-time dialogues. Unlike traditional mentoring, this method allows scaling training, making it accessible to a large number of employees regardless of their location and time constraints [10].
The application of digital twins in training allows significantly reducing the time needed for new employees adaptation and improving their professional skills. Data analysis from several large corporations has shown that the use of digital mentoring reduces the time required to master new job responsibilities by an average of 35%, and also improves the accuracy of task completion by 22% [11]. The data obtained from the comparative study is presented in the following table (Table 2).
Table 2
Comparative analysis of employee adaptation time in traditional and digital mentoring
| Indicator | Traditional mentoring | Digital mentoring | Difference in indicators |
| Average adaptation time (weeks) | 12 | 7 | -5 weeks (-42%) |
| Task accuracy level (%) | 78 | 95 | +17% |
| Percentage of employees successfully adapted (%) | 70 | 88 | +18% |
| Overall satisfaction level (%) | 65 | 90 | +25% |
Traditional mentoring involves a lengthy adaptation period – on average, 12 weeks. During this time, the accuracy of task completion is 78%, and the percentage of employees successfully completing the adaptation process is 70%. This indicates that traditional methods require significant time investments and do not always provide a high level of training.
Digital mentoring shows a significant reduction in adaptation time – down to 7 weeks, which is 42% faster compared to the traditional approach. At the same time, task completion accuracy increases to 95%, and the percentage of successfully adapted employees rises to 88%. This method also significantly boosts employee satisfaction – 90% versus 65% for traditional mentoring.
The analysis results demonstrate that digital mentoring significantly outperforms traditional mentoring methods on all key parameters. It allows for reducing the adaptation period, improving task accuracy, and enhancing employee engagement. This is explained by the use of personalized learning algorithms, constant feedback, and the availability of the digital mentor at any time.
Thus, innovative approaches to employee training, such as learning through provocation and digital mentoring, show great potential in rapidly changing environments. They not only transmit knowledge but also develop critical skills in employees, which are necessary for working in conditions of uncertainty and constant technological updates.
Conclusion
The conducted research allowed for identifying the main trends in digital transformation within corporate training and evaluating their impact on the effectiveness of professional development for employees. The analysis showed that the use of mobile, adaptive, and immersive learning contributes to increasing access to knowledge and improving employee involvement in the educational process. At the same time, the implementation of digital technologies is accompanied by certain psychological and organizational barriers that require a comprehensive approach to overcoming them.
The innovative methods discussed, such as learning through provocation and mentoring with digital twins, demonstrate significant advantages over traditional approaches. Learning through provocation helps develop critical thinking, flexibility, and adaptability by engaging employees in non-standard situations. Meanwhile, digital mentoring reduces adaptation time, improves task accuracy, and enhances overall employee satisfaction with the learning process. These methods confirm the effectiveness of personalized and interactive strategies in modern educational systems.
The results obtained indicate the need for further development of digital solutions in corporate learning. Promising research directions could include the integration of artificial intelligence technologies for deep personalization of training programs, the development of new forms of immersive learning, and the analysis of the long-term effects of digital methods on employee professional development. It is important to consider organizational and cultural factors when implementing new educational solutions to ensure their successful adoption and maximize their effectiveness.
Библиографический список
1. Baisova G. Integration of Artificial Intelligence into Educational Programs to Develop Scientific Analysis Skills in a Multidisciplinary Environment // Bulletin of Science and Practice. – 2024. – Vol. 10. – No. 11. – P. 410-416.2. Zhang J., Chen Z. Exploring human resource management digital transformation in the digital age // Journal of the knowledge economy. – 2024. – Vol. 15. – No. 1. – P. 1482-1498.
3. Muradaliyeva E.E. Innovative methods of personnel management in the conditions of digitalization of the economy // Bulletin of the Rostov state economic university (RINH). – 2022. – No. 4 (80). – P. 207-211.
4. Kamakin A.V. Innovative trends in personnel management of enterprises in Russia // International journal of humanities and natural sciences. – 2023. – No. 4-2 (79). – P. 14-16.
5. Abramov V.I., Glukhova E.V. Retraining and professional development of personnel in the context of the digital transformation of the economy // Development of the labor market in the modern stage of socio-economic transformations. – 2021. – P. 3-10.
6. Blanka C., Krumay B., Rueckel D. The interplay of digital transformation and employee competency: A design science approach // Technological forecasting and social change. – 2022. – Vol. 178. – P. 15.
7. Baisova G. The impact of artificial intelligence on the development of critical thinking in the process of learning STEM disciplines // Cold Science. – 2024. – No. 8. – P. 47-55.
8. Serpik Z.P. Digital transformation of HR: How new technologies are changing approaches to talent management and employee engagement // Scientific works of the Moscow humanitarian university. – 2025. – No. 6.
9. Goulart V.G., Liboni L.B., Cezarino L.O. Balancing skills in the digital transformation era: The future of jobs and the role of higher education // Industry and higher education. – 2022. – Vol. 36. – No. 2. – P. 118-127.
10. Trenerry B., Chng S., Wang Y., Shah S.Z., Lim S.S., Lu H.Y., Oh P.H. Preparing workplaces for digital transformation: An integrative review and framework of multi-level factors // Frontiers in psychology. – 2021. – Vol. 12. – P. 24.
11. Alenezi M. Deep dive into digital transformation in higher education institutions // Education sciences. – 2021. – Vol. 11. – No. 12. – P. 770.
